How to operate a drone introduces the exciting world of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), also known as drones. This guide delves into the essential aspects of drone operation, from understanding fundamental regulations and safety protocols to mastering advanced flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial photography. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone components, flight controls, and troubleshooting common issues, empowering you to confidently take to the skies.
Whether you’re a novice eager to learn the basics or an experienced pilot seeking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource provides a step-by-step approach to safe and efficient drone operation. We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and legal requirements to advanced maneuvers and post-flight maintenance, ensuring a thorough understanding of this increasingly popular technology.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to relevant regulations and safety procedures. Failure to do so can result in accidents, fines, and legal repercussions. This section Artikels key aspects of safe and legal drone operation.
FAA Regulations for Drone Operation
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States regulates drone operation within its airspace classes. These classes, from A to G, dictate altitude restrictions, required pilot certifications, and operational limitations. Class G airspace, for example, is generally uncontrolled airspace where simpler regulations apply, while Class B airspace, surrounding major airports, necessitates more stringent requirements and potentially requires specific authorization.
Understanding the airspace class before flight is crucial for safe and legal operation.
Drone Flight Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation involves a comprehensive pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight checklist. This ensures the drone’s operational readiness and minimizes risks.
- Pre-flight: Check battery levels, GPS signal strength, weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation), and ensure all components are securely attached. Inspect propellers for damage.
- In-flight: Maintain visual line of sight with the drone at all times, unless operating under specific exemptions. Avoid flying near people, buildings, or obstacles. Be mindful of other aircraft and adhere to airspace restrictions.
- Post-flight: Power down the drone, securely store the battery, and review flight logs to identify potential issues or areas for improvement. Inspect the drone for any damage.
Drone Preflight Checklist
| Item | Check | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Sufficient charge (at least 20% remaining) | Charge battery if needed |
| GPS Signal | Strong signal, sufficient satellites locked | Relocate to an area with better signal if necessary |
| Weather Conditions | Wind speed below recommended limits, no precipitation | Postpone flight if conditions are unfavorable |
| Propeller Inspection | No damage or cracks | Replace damaged propellers |
Examples of Drone Accidents and Prevention
Common drone accidents include collisions with obstacles, loss of control due to low battery or signal interference, and crashes due to unexpected weather changes. These accidents can often be prevented through thorough pre-flight checks, adherence to safety guidelines, and the use of appropriate safety features such as Return-to-Home (RTH) functionality.
Drone Licenses and Permits Comparison
| License/Permit | Requirements | Restrictions | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recreational | Registration with the FAA (if applicable) | Weight and operational limitations | Free (registration fee may apply) |
| Part 107 (Commercial) | Written exam, background check | Operational limitations based on airspace class and certifications | Exam fee, renewal fees |
| Special Authorization | Application, specific requirements based on operation | Highly specific to operation | Varies based on requirements |
| Waiver | Application demonstrating need for exemption | Exemption from specific regulations | Varies based on requirements |
Understanding Drone Components and Controls
A drone’s functionality relies on the integrated operation of several key components. Understanding their roles is essential for safe and effective operation and troubleshooting.
Drone Components and Their Functions
Typical drone components include propellers, motors, a flight controller, a battery, a camera, and a GPS module. Propellers generate thrust, motors provide power, the flight controller manages stability and flight maneuvers, the battery provides power to the system, the camera captures images and videos, and the GPS module aids in navigation and positioning.
Types of Drone Controllers and Functionalities
Drone controllers vary in design and functionality. Some are simple, offering basic flight controls, while others incorporate advanced features such as GPS navigation, obstacle avoidance, and intelligent flight modes. The choice of controller depends on the drone’s capabilities and the user’s experience level. Many controllers now offer touchscreen interfaces for intuitive control and configuration.
Drone User Interfaces Comparison
User interfaces differ significantly across drone models. Some feature simple, intuitive interfaces, while others are more complex and require more training. Factors to consider include screen size, responsiveness, and the availability of customizable settings and flight modes. A user-friendly interface greatly enhances the overall flying experience.
Drone Sensor and GPS Calibration
Accurate sensor and GPS calibration is crucial for stable and precise flight. This process involves leveling the drone, ensuring proper GPS signal acquisition, and potentially running automated calibration routines provided by the drone’s software. The specific steps vary based on the drone model and manufacturer.
Step-by-Step Drone Assembly Guide
- Carefully unpack all drone components and verify their completeness against the manufacturer’s checklist.
- Attach the propellers to the motors, ensuring they are correctly oriented.
- Securely connect the battery to the drone’s power port.
- Power on the drone and controller and verify communication between the two devices.
- Calibrate the drone’s sensors and GPS according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Perform a pre-flight check before initiating the first flight.
Flight Techniques and Maneuvers
Mastering basic flight controls and maneuvers is fundamental to safe and efficient drone operation. This section covers essential techniques for beginners and experienced pilots alike.
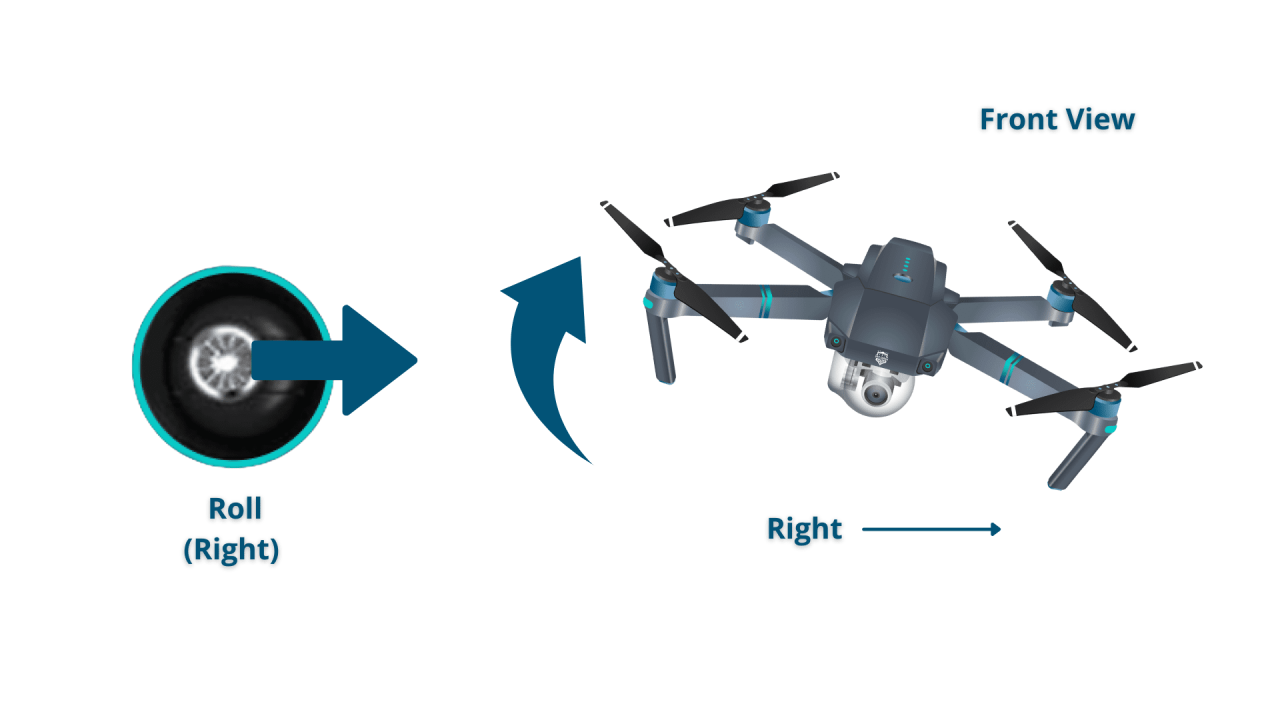
Basic Drone Flight Controls
The basic flight controls typically involve throttle (altitude control), yaw (rotation around the vertical axis), pitch (forward/backward movement), and roll (left/right movement). Understanding how these controls interact is crucial for smooth and controlled flight. Most drones use joysticks or a combination of joysticks and buttons to control these parameters.
Drone Takeoff, Hover, and Landing Procedures
Safe takeoff, hovering, and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents. Takeoff should be performed in an open area with ample space, ensuring a stable hover before initiating any maneuvers. Landing should be slow and controlled, with a gentle descent to the ground. Practice these maneuvers in a safe and controlled environment before attempting more advanced techniques.
Tips for Smooth and Controlled Drone Maneuvers
Smooth and controlled maneuvers require practice and a delicate touch. Avoid abrupt movements, especially in windy conditions. Using the drone’s assisted flight modes (if available) can help maintain stability and prevent unintended movements. Gradually increase the complexity of maneuvers as your skills improve.
Flying Drones in Windy Conditions

Windy conditions present challenges to drone stability and control. It’s crucial to check wind speeds before flight and avoid flying in strong winds. If flying in light to moderate winds is unavoidable, adjust flight parameters and maintain a closer visual line of sight. Using the drone’s Return-to-Home (RTH) function can be helpful in case of unexpected wind gusts.
Example Flight Plan for Aerial Photography
A flight plan for aerial photography of a building might involve pre-flight checks, establishing a safe flight path, positioning the drone for optimal camera angles (e.g., establishing shots from various elevations and perspectives), capturing images, and a controlled landing. The specific flight plan will depend on the building’s size, location, and surrounding environment.
Drone Photography and Videography: How To Operate A Drone
Drones offer unique perspectives for photography and videography. This section explores techniques for capturing high-quality aerial footage.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Image Quality
Camera settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO significantly impact image quality. Aperture controls depth of field, shutter speed affects motion blur, and ISO determines image sensitivity to light. Understanding how these settings interact allows for fine-tuning image quality to suit various lighting conditions and creative goals. Experimentation and practice are key to mastering these settings.
Techniques for Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Capturing high-quality aerial footage requires careful planning and execution. Consider factors such as lighting, composition, and camera movement. Smooth, controlled movements are essential for minimizing camera shake and producing professional-looking results. Using the drone’s gimbal (if equipped) helps to stabilize the camera and improve image quality.
Different Camera Angles and Shots Achievable with a Drone
Drones allow for a wide variety of camera angles and shots, including high-angle shots, low-angle shots, tracking shots, and orbiting shots. Experimenting with different angles and perspectives allows for creative storytelling and capturing unique perspectives that are not achievable from ground level. Understanding the possibilities expands creative potential.
Using Filters and Editing Software to Enhance Drone Footage
Filters and editing software can enhance the visual appeal of drone footage. Filters can correct color balance, add creative effects, and improve image sharpness. Editing software allows for adjustments to brightness, contrast, saturation, and other parameters. Careful use of these tools can greatly improve the overall quality and aesthetic appeal of the footage.
Guide on Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Composing compelling aerial shots involves applying fundamental photography principles, such as the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry. Understanding these principles allows for creating visually engaging images that effectively convey a message or tell a story. Practice and experimentation are key to developing a strong compositional eye.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful operation, drones can experience problems. This section provides guidance on troubleshooting common issues.
Identifying Common Drone Problems
Common drone problems include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor malfunctions, and communication issues between the drone and controller. Understanding the symptoms of these problems is the first step towards effective troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Steps for Resolving Common Drone Issues
Troubleshooting steps vary depending on the specific problem. For example, low battery can be addressed by charging the battery, while GPS signal loss might require relocating to an area with better signal reception. Motor malfunctions may require replacing a faulty motor or other component. Consulting the drone’s manual or manufacturer’s website is often helpful in resolving specific issues.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone and ensure safe and responsible operation. Ultimately, consistent practice and understanding the limitations of your drone are essential for proficient operation.
Performing Basic Drone Maintenance
Basic drone maintenance involves regular cleaning, inspecting for damage, and lubricating moving parts (as needed). Proper maintenance extends the drone’s lifespan and prevents potential problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for maintenance procedures.
Interpreting Error Messages Displayed on the Drone Controller, How to operate a drone
Drone controllers often display error messages to indicate specific problems. Understanding these messages is crucial for diagnosing and resolving issues. Refer to the drone’s manual for explanations of specific error codes.
Preventative Measures to Avoid Common Drone Problems
Preventative measures include regular maintenance, careful handling, and avoiding extreme weather conditions. Proper battery care and storage are also crucial for preventing battery-related problems. Following safety guidelines and best practices minimizes the risk of accidents and reduces the likelihood of encountering common drone issues.
Drone Battery Management and Safety
Proper battery management is crucial for safe and reliable drone operation. This section details safe handling and charging procedures.
Importance of Proper Battery Care and Handling
Drone batteries are sensitive components that require careful handling to ensure safety and longevity. Avoid dropping, puncturing, or crushing the batteries. Always store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials.
Safe Charging Procedures for Drone Batteries

Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow the charging instructions carefully. Never leave batteries unattended while charging. Ensure the charging environment is well-ventilated to prevent overheating. Overcharging can damage the battery and potentially pose a fire hazard.
Signs of a Damaged or Faulty Battery
Signs of a damaged or faulty battery include swelling, leaking, unusual heating, or reduced flight time. If you observe any of these signs, discontinue use of the battery immediately and replace it.
Tips for Extending the Lifespan of Drone Batteries
To extend battery lifespan, avoid completely depleting the battery before charging, store batteries at a moderate temperature, and avoid extreme temperature fluctuations. Proper storage and charging habits contribute significantly to battery longevity.
Visual Guide Illustrating Safe Battery Handling and Storage Procedures
- Always handle batteries gently, avoiding dropping or crushing them.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Never leave batteries unattended while charging.
- Use only the manufacturer’s recommended charger.
- Inspect batteries regularly for signs of damage (swelling, leaks, etc.).
- Dispose of damaged or faulty batteries properly, according to local regulations.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has equipped you with the foundational understanding needed to navigate the complexities of drone flight safely and effectively. Remember that continuous learning and adherence to safety regulations are paramount. As you gain experience, explore the vast creative possibilities of aerial photography and videography, while always prioritizing safety and responsible drone operation.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety procedures. A crucial step is familiarizing yourself with the regulations governing drone operation in your area. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills will allow you to safely and effectively operate your drone, capturing stunning aerial footage or completing various tasks.
FAQ Overview
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a ready-to-fly (RTF) drone with GPS stabilization and autonomous features is recommended. These drones offer ease of use and enhanced stability.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s sensors?
It’s advisable to calibrate your drone’s sensors before each flight, particularly after a crash or significant impact. Refer to your drone’s manual for specific calibration instructions.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately initiate a safe return-to-home (RTH) procedure if available. If RTH is unavailable, carefully bring the drone down manually, prioritizing safety.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies depending on the model, battery capacity, and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, but always check your drone’s specifications.
